Introduction



Satellite-based remote sensing supports a number of applications related to atmospheric composition.
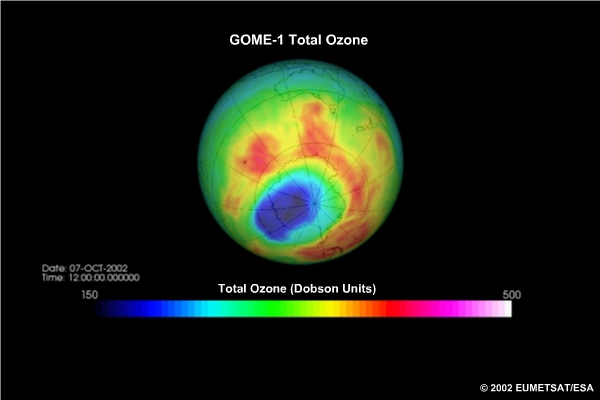
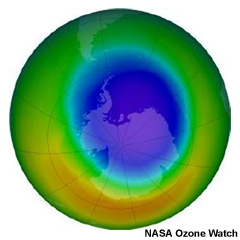
The best-known application with the longest established contribution from satellites is stratospheric ozone monitoring. This continues to be important as we monitor the anticipated recovery of the ozone layer.
In addition, tracking long-range pollution transport is an application ideally suited to satellites, which can potentially provide global coverage on a daily basis.
Monitoring air quality
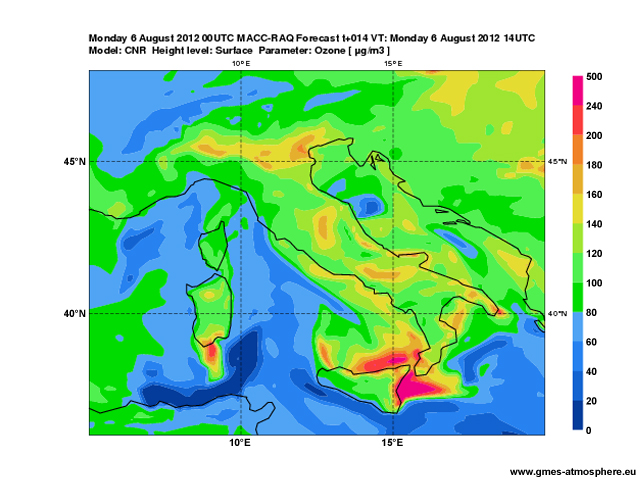
With recent advances in space-based instrumentation and retrieval techniques, satellite data now support air quality monitoring both at global and regional scales.

Monitoring biomass burning

Monitoring volcanic eruptions
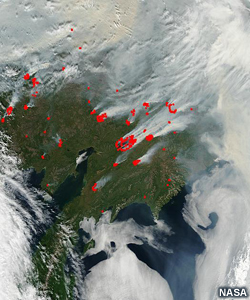
Monitoring wildfire emissions
Satellites also make important contributions to monitoring biomass burning, fire emissions, and volcanic eruptions.

Monitoring wildfire emissions
Satellites also make important contributions to monitoring biomass burning, fire emissions, and volcanic eruptions.


With the increasing urgency to observe and understand climate change, monitoring greenhouse gases to help estimate surface fluxes is an emerging field.
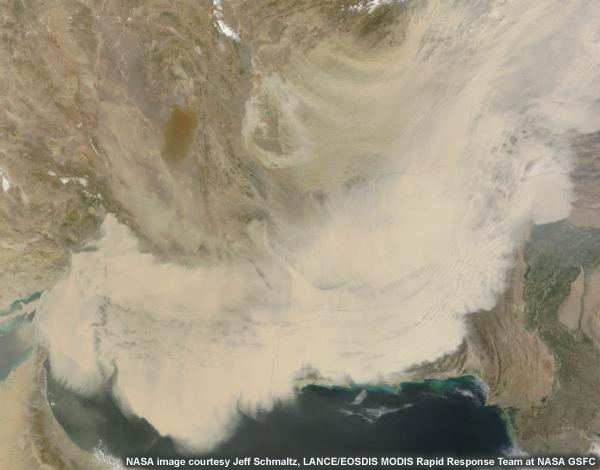

Improved knowledge about the role of aerosols in climate change is also a pressing area of scientific research to which satellite data can contribute.
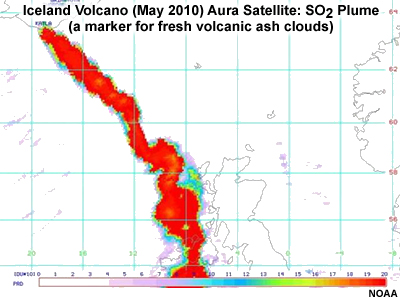
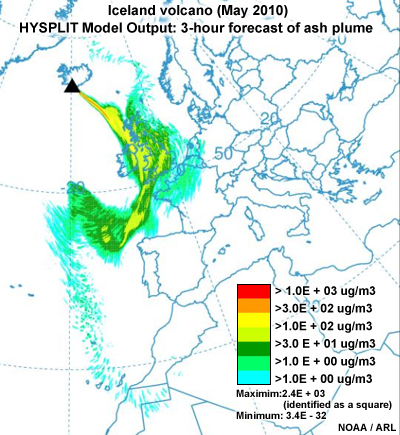
This module focuses on the uses of satellite observations for monitoring and forecasting atmospheric composition. We will also summarize the development of related operational applications and services. Although not discussed here, note that surface and ground-based remote sensing networks provide an important component of the observing system, and many detailed research activities underpin the development of longer term operational services.