Volcanic Hazards » Volcanic Gases
Magma contains dissolved gases that are released into the atmosphere during eruptions. Gases are also released from magma that either remains below ground or rises toward the surface. Gases may escape continuously into the atmosphere from the soil, volcanic vents, fumaroles, and hydrothermal systems. The most common gases released are:
- Water Vapor (H2O)
- CO2 (carbon dioxide): when trapped in depressions can be lethal to people, and animals
- SO2 (sulfur dioxide): causes air pollution, and affects Earth’s surface temperature
- H2S (hydrogen sulfide): may cause eye, nose, throat irritation and breathing difficulty, as well as headaches and dizziness
- (HCl) hydrogen chloride: may cause acid rain downwind, and exposure irritates eyes and respiratory tract
See http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/hazards/gas/index.php for more information.
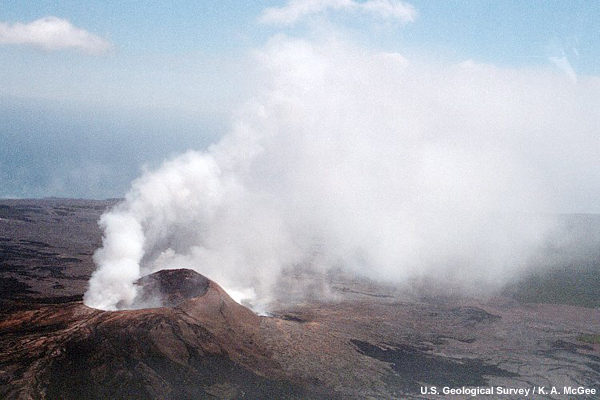

Sulfur dioxide and other volcanic gases rise from the Pu`u `O`o vent on Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii. (U.S. Geological Survey)